Cryptographic Key Generation Using Biometrics
Posted By admin On 17.12.20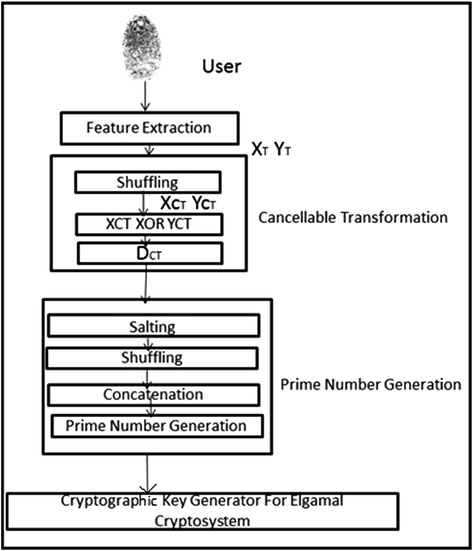
- W. Stallings, Cryptography and Network Security: Principles and Practice, 5th edition, Prentice Hall, 2010.Google Scholar
- Soutar, C.; Roberge, A. and Vijaya Kumar, B.V.K., “Biometric Encryption using Image Processing”, SPIE, pp. 178–188, 1998.Google Scholar
- Bolle, R.M.; Connel, J.H. and Ratha, N.K., “Biometrics Perils and Patches”, Elsevier - Pattern Recognition 35, pp. 2727–2738, 2002.Google Scholar
- Teoh, Andrew B.J.; Goh, A. and Ngo, D.C.L., “Random MultispaceQuantisation as an Analytic Mechanism for BioHashing of Biometric and Random Identity Inputs”, IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 28(12), pp. 1892–1901, 2006.Google Scholar
- Ratha, N.K.; Chikkerur, S.; Connell, J.H. and Bolle, R.M., “Generating Cancelable Fingerprint Templates”, IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 29(4), pp. 561–572, 2007.Google Scholar
- Tulyakov, S.; Farooq, F. and Govindaraju, V., “Symmetric Hash Functions for Fingerprint Minutiae”, International Workshop on Pattern Recognition for Crime Prevention, Security and Surveillance (ICAPR 2005), 3687, pp. 30–38, 2005.Google Scholar
- Ang, R.; Rei, S.N. and McAven, L., “Cancelable Key-Based Fingerprint Templates”, Information Security and Privacy: 10th Australasian Conference (ACISP 2005), pp. 242–252, 2005.Google Scholar
- Maiorana, E.; Campisi, P.; Fierrez, J. and Ortega-Garcia, J., “Cancelable Templates for Sequence Based Biometrics with Application to On-line Signature Recognition”, IEEE Transactions on Systems, 40(3), pp. 525–538, 2010.Google Scholar
- Nanni, L. and Lumini, A., “Cancelable Biometrics: Problems and Solutions for Improving Accuracy”, NovaPublisher - Biometrics: Methods, Applications and Analysis, chap-7, pp. 153–166, 2010.Google Scholar
- F Monrose, MK Reiter, Q Li, S Wetzel, “Cryptographic key generation from voice”, Proceedings of IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy, pp. 202–213, 2011.Google Scholar
- H Feng, CC Wah, “Private Key generation from on-line hand written signatures”, Information Management & Computer Security, 10(4), pp. 159–164, 2002.Google Scholar
- B Chen, V Chandran, “Biometric Based Cryptographic Key Generation from Faces”, Proceedings of 9th Biennial Conference of the Australian Pattern Recognition Society on Digital Image Computing Techniques and Applications, pp. 394–401, 2007.Google Scholar
- A Jagadeesan, K Duraiswamy, “Secured Cryptographic Key Generationfrom Multimodal Biometrics: Feature Level Fusion of Fingerprint and Iris”, Int. Journalon Computer Sc. & Information Security, 7(2), pp. 28–37, 2010.Google Scholar
- A Jagadeesan, T Thillaikkarasi, K Duraiswamy, “Cryptographic KeyGeneration from Multiple Biometrics Modalities: Fusing Minutiae with Iris Feature”, Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2(6), pp. 16–26, 2010.Google Scholar
- C Rathgeb, A Uhl., “Context-based biometric key generation for Iris”, IET Computer Vision, 5(6), pp. 389–397, 2011.Google Scholar
- D. Milao Q. Tang, and W. Fu, “Fingerprint minutia extraction based on principal curves,” Pattern Recognition Letters, Vol. 28, Issue 16, pp. 2184–2189, 2009.Google Scholar
The beauty of using biometrics to lock your secret key is that, like all other cryptographic solutions on Android, all sensitive operations between the biometrics system and the Android Keystore. The construction of cryptographic key from biometrics is used to make safe our system. To implement this concept, sender’s recent fingerprint would be used to construct key by combining it. Feng Hao et al. 31 have presented a biometric based cryptographic key generation method utilizing the iris feature. From legitimate iris codes, a recurring binary string termed as biometric key was created which is more reliable. Fallout 4 steam key generator. Auxiliary error-correction data, that does not unvei006C the key and can be accumulated in a tamper-resistant.
Cryptographic Key Generation Using Biometrics System
The generation of cryptographic key from individual user’s biometric feature is a solution to this problem. In this approach, it is too hard for the attacker to guess the cryptographic key without the prior knowledge of the user’s biometrics. But the problem with biometrics is that compromise makes it unusable. Efficient Cryptographic Key Generation Using Fingerprint Ginu Thomas, K.Rahimunnisa, Sonima Parayil Abstract— T Biometrics are used for the high secure applications in cryptography. Cryptography is intended to ensure the secret and authenticity of a message. Several biometrics like fingerprint, iris, retina, etc., are used in rendering security to the information or key. The generation of cryptographic key from biometrics is used generally to secure. Be addressed in a wide range of applications by generating strong cryptographic keys from biometric data, possibly in conjunctionwith the entry of a password 24, 3, 9, 15. This approach is attractive since it imposes no additional mem-orization on the user and yet can yield keys significantly stronger than passwords. These keys could then be.